Applications
Video Thumbnails
EXR Viewer
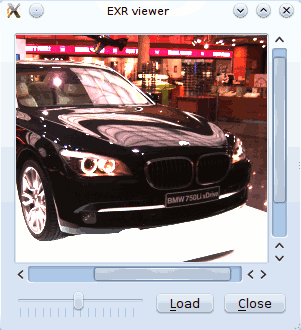
This is small viewer for displaying EXR images. The exposure can be modified with the slider.
The user interface was defined using Qt-Designer. The scroll area was defined by promoting a QFrame object to QScrollArea. See reference about using custom widgets for more information.
To use this application you need to install Qt4Ruby. You also need to compile the user interface description file first:
rbuic4 exrviewer.ui > ui_exrviewer.rb
The UI file is available for download here: exrviewer.ui
require 'hornetseye_openexr'
require 'hornetseye_qt4'
require_relative 'ui_exrviewer'
include Hornetseye
class EXRViewer < Qt::Widget
slots 'load()'
slots 'recompute()'
def initialize( parent = nil )
super parent
@ui = Ui::EXRViewer.new
@ui.setupUi self
connect @ui., SIGNAL('clicked()'), self, SLOT('close()')
connect @ui., SIGNAL('clicked()'), self, SLOT('load()')
connect @ui., SIGNAL('valueChanged(int)'),
self, SLOT('recompute()')
@arr = nil
@channelmax = nil
@label = Qt::Label.new
@ui.scroll_area.setWidget @label
end
def load
fileName = Qt::FileDialog.getOpenFileName self, "Load EXR File", "",
"EXR image (*.exr)"
if fileName
@arr = MultiArray.load_sfloatrgb fileName
@max = proc { |x| [x.r, x.g, x.b].max }.call @arr.max
@ui..setEnabled true
recompute
end
end
def recompute
factor = 2.0 ** (@ui..value / 4096.0) * 0xFF / @max
img = (@arr * factor).minor(0xFF).to_ubytergb
qimage = Qt::Image.new img.memory.export, img.width, img.height, Qt::Image::Format_RGB888
pixmap = Qt::Pixmap.new
pixmap.convertFromImage qimage
@label.setPixmap pixmap
@label.resize pixmap.width, pixmap.height
end
end
app = Qt::Application.new ARGV
viewer = EXRViewer.new
viewer.show
app.exec
XVideo Widget
The XVideo widget allows to use XVideo acceleration in a Qt4-QtRuby application. The example application shows how to write a small program for playing videos.
require 'hornetseye_ffmpeg'
require 'hornetseye_alsa'
require 'hornetseye_qt4'
VIDEO = ARGV.first || 'http://peach.themazzone.com/durian/movies/sintel-1024-surround.mp4'
class Win < Qt::Widget
slots 'seek(int)'
def initialize
super
@screen = Hornetseye::XvWidget.new self
@slider = Qt::Slider.new Qt::Horizontal
layout = Qt::VBoxLayout.new self
layout.addWidget @screen
layout.addWidget @slider
connect @slider, SIGNAL('valueChanged(int)'), self, SLOT('seek(int)')
@seeking = true
@video = nil
@timer = 0
start
@slider.tracking = false
@slider.minimum = 0
@slider.single_step = 60
@slider.page_step = 600
if @video.duration
@slider.maximum = @video.duration.to_i
else
@slider.maximum = ARGV[1] || 1
end
setWindowTitle 'XVideo'
end
def update_audio
@audio_frame = @video.read_audio unless @audio_frame
while @speaker.delay < @speaker.rate / 4
@speaker.write @audio_frame
@audio_frame = @video.read_audio
end
end
def update_video
@screen.write @video.read_video
end
def timerEvent( e )
begin
update_audio if @video.has_audio?
update_video
unless @slider.
@seeking = false
p = @video.video_pos.to_i
@slider.maximum = p if p > @slider.maximum
@slider.value = p
@seeking = true
end
if @video.has_audio?
t = @video.audio_pos - (@speaker.delay + @audio_frame.shape[1]).quo( @speaker.rate )
delay = [ 3.quo( 2 ) / @video.frame_rate, [ @video.video_pos - t, 0 ].max ].min
killTimer @timer
@timer = startTimer( ( delay * 1000 ).to_i )
end
rescue Exception => e
p e
stop
end
end
def start
unless @video
stop
@video = Hornetseye::AVInput.new VIDEO
@audio_frame = nil
resize (@video.width * @video.aspect_ratio).to_i, @video.height
if @video.has_audio?
@speaker = Hornetseye::AlsaOutput.new 'default', @video.sample_rate, @video.channels
@timer = startTimer 0
else
@speaker = nil
@timer = startTimer((1000 / @video.frame_rate).to_i)
end
end
end
def stop
@audio_frame = nil
if @video
@video.close
@video = nil
end
if @speaker
@speaker.close
@speaker = nil
end
if @timer != 0
killTimer @timer
@timer = 0
@screen.clear
end
end
def seek( p )
if @seeking
begin
start
@audio_frame = nil
@video.pos = p
if @speaker
@speaker.drop
end
rescue Exception => e
p e
stop
end
end
end
end
app = Qt::Application.new ARGV
Win.new.show
app.exec
Webcam Viewer
This is an example using an XVideo widget to implement a webcam viewer. The viewer also has controls for a few camera features.
To use this application you need to install Qt4Ruby. You also need to compile the user interface description files first:
rbuic4 modedialog.ui > ui_modedialog.rb
rbuic4 webcam.ui > ui_webcam.rb
The UI files are available for download here: webcam.ui, modedialog.ui
require 'hornetseye_v4l2'
require 'hornetseye_qt4'
require_relative 'ui_modedialog'
require_relative 'ui_webcam'
include Hornetseye
app = Qt::Application.new ARGV
class ModeDialog < Qt::Dialog
def initialize(parent = nil)
super parent
@ui = Ui::ModeDialog.new
@ui.setupUi self
end
def clear_modes
@ui.modeList.clear
end
def add_mode(typecode, width, height)
@ui.modeList.addItem "#{typecode} #{width} x #{height}"
end
def selected
@ui.modeList.currentRow
end
end
class Webcam < Qt::Dialog
slots 'open_camera(bool)'
slots 'select_feature(int)'
slots 'set_feature(int)'
def initialize(parent = nil)
super parent
@ui = Ui::WebcamWindow.new
@ui.setupUi self
@xvwidget = XvWidget.new
@ui.scrollArea. = @xvwidget
connect @ui.connectButton, SIGNAL('toggled(bool)'), self, SLOT('open_camera(bool)')
connect @ui.featureCombo, SIGNAL('currentIndexChanged(int)'),
self, SLOT('select_feature(int)')
connect @ui.featureSlider, SIGNAL('valueChanged(int)'),
self, SLOT('set_feature(int)')
@input = nil
@timer = 0
@features = []
@mode_dialog = ModeDialog.new
end
def open_camera(on)
begin
if on
@ui.errorLabel.text = ''
@input = V4L2Input.new @ui.deviceEdit.text do |modes|
@mode_dialog.clear_modes
modes.each { |mode| @mode_dialog.add_mode *mode }
raise 'Opening camera was aborted' unless @mode_dialog.exec == Qt::Dialog::Accepted
modes[@mode_dialog.selected || 0]
end
@input.read
for feature in V4L2Input::FEATURE_BASE .. V4L2Input::FEATURE_LASTP1
if @input.feature_exist? feature
@features << feature
@ui.featureCombo.addItem @input.feature_name(feature)
end
end
@ui.featureCombo.enabled = true
@ui.deviceEdit.enabled = false
@timer = startTimer 0
else
killTimer @timer if @timer != 0
if @input
@input.close
@input = nil
end
@features = []
@ui.featureCombo.clear
@ui.deviceEdit.enabled = true
@ui.featureCombo.enabled = false
end
rescue RuntimeError => e
@ui.errorLabel.text = e.to_s
@ui.connectButton.checked = false
end
end
def select_feature(value)
if @input and value >= 0
feature = @features[value]
@input, input = nil, @input
@ui.featureSlider.minimum = input.feature_min feature
@ui.featureSlider.maximum = input.feature_max feature
@ui.featureSlider.value = input.feature_read feature
@ui.featureSlider.enabled = true
@input = input
else
@ui.featureSlider.enabled = false
end
end
def set_feature(value)
if @input
@input.feature_write @features[@ui.featureCombo.currentIndex], value
end
end
def timerEvent( e )
begin
@xvwidget.write @input.read
rescue RuntimeError => e
@ui.errorLabel.text = e.to_s
@ui.connectButton.checked = false
end
end
end
win = Webcam.new
win.show
app.exec
2D Plot
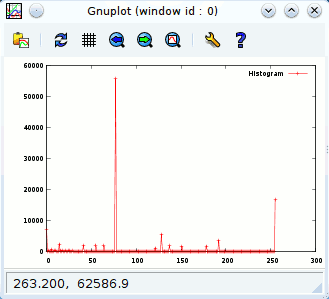
With Gordon James Miller’s rgplot package you can use Gnuplot from within Ruby. This example shows how you can plot the histogram of an image.
require 'hornetseye_rmagick'
require 'gnuplot'
include Hornetseye
def plot( *arrs )
= arrs.last.is_a?( Hash ) ? arrs.pop : {}
{ :title => [ nil ] * arrs.size }.merge
title = [ :title ]
title = [ title ] unless title.is_a? Array
Gnuplot.open do |gp|
Gnuplot::Plot.new( gp ) do |plot|
arrs.zip( title ).each do |arr,t|
x = (0...arr.size).collect { |v| v.to_f }
plot.data << Gnuplot::DataSet.new( [ x, arr ] ) do |ds|
ds.with = "linespoints"
if t
ds.title = t
else
ds.notitle
end
end
end
end
end
nil
end
img = MultiArray.load_ubyte 'http://www.wedesoft.de/hornetseye-api/images/grey.png'
plot img.histogram( 256 ), :title => [ 'Histogram' ]
3D Plot
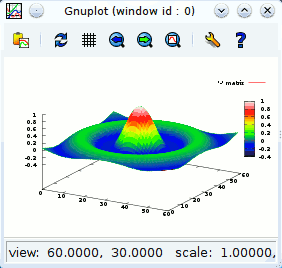
This example shows how you can use Gnuplot to make a 3D plot of a two-dimensional array.
require 'multiarray'
require 'gnuplot'
include Hornetseye
class Node
def to_gsplot
retval = ""
for j in 0...shape[1]
for i in 0...shape[0]
retval += " #{self[i,j]}"
end
retval += "\n"
end
retval += "\n"
retval
end
def plot
Gnuplot.open do |gp|
Gnuplot::SPlot.new( gp ) do |plot|
plot.pm3d
plot.hidden3d
plot.palette 'defined ( 0 "black", 51 "blue", 102 "green", ' +
'153 "yellow", 204 "red", 255 "white" )'
plot.data << Gnuplot::DataSet.new( self ) do |ds|
ds.with = 'lines'
ds.matrix = true
end
end
end
end
end
s = lazy( 60 ) { |i| ( i + 0.5 - 60 / 2 ) / Math::PI }
sinc = finalise do |i,j|
r = Math.hypot s[i], s[j]
Math.sin( r ) / r
end
sinc.plot
Depth from Focus
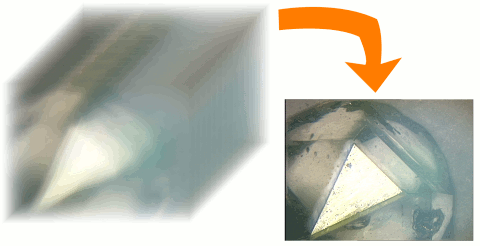
This is an implementation of depth of focus. The Sobel gradient magnitude of the focus stack is used as a sharpness measure. An image with extended depth of field is created (deep view). Furthermore a height field is generated. With POVRay the height field and the deep view can be used to generate a 3D rendering.
Note that the trollop Ruby-extension is required for parsing the command line.
require 'hornetseye_rmagick'
require 'hornetseye_xorg'
require 'trollop'
include Hornetseye
opts = Trollop:: do
<<EOS
Generate height field and deep view from focus stack.
Usage:
./depthfromfocus.rb [options] <file names>+
where [options] are:
EOS
opt :sigma, 'Sigma for Gaussian blur (1/pixelsize)', :default => 2.5
opt :field, 'Output PGM file name for height field', :type => String
opt :view, 'Output PPM file name for deep view', :type => String
opt :alternative, 'Threat later half of filenames as alternative focus ' +
'stack to generate deep view'
end
sigma = opts[ :sigma ]
Trollop::die :sigma, 'must be greater than zero' unless sigma > 0
field_file = opts[ :field ]
Trollop::die :field, 'is required' unless field_file
view_file = opts[ :view ]
Trollop::die :view, 'is required' unless view_file
alternative = opts[ :alternative ]
if alternative
if ARGV.size % 2 != 0
Trollop::die 'Even number of file names required when using alternative ' +
'focus stack'
end
n = ARGV.size / 2
stack_file = ARGV.slice! 0, n
alternative_file = ARGV.slice! 0, n
else
stack_file = ARGV
alternative_file = nil
end
Trollop::die 'Cannot handle more than 255 files' if stack_file.size > 255
display = X11Display.new
field_output = XImageOutput.new
view_output = XImageOutput.new
field_window = X11Window.new display, field_output, 320, 240
view_window = X11Window.new display, view_output, 320, 240
field, view, max_sharpness = nil, nil, nil
stack_file.each_with_index do |f_name,i|
img = MultiArray.load_ubytergb f_name
if field
if img.shape != field.shape
raise "Image '#{f_name}' must be of size #{field.shape[0]}x" +
"#{field.shape[1]} (but was #{img.shape[0]}x#{img.shape[1]})"
end
else
field = MultiArray.ubyte( *img.shape ).fill!
view = MultiArray.ubytergb( *img.shape ).fill!
max_sharpness = MultiArray.dfloat( *img.shape ).fill!
field_window.resize *img.shape
view_window.resize *img.shape
field_window.show
view_window.show
end
sharpness = ( img.sobel( 0 ) ** 2 +
img.sobel( 1 ) ** 2 ).to_dfloat.gauss_blur sigma
mask = sharpness > max_sharpness
field = mask.conditional i, field
if alternative
alternative_img = MultiArray.load_ubytergb alternative_file[ i ]
view = mask.conditional alternative_img, view
else
view = mask.conditional img, view
end
max_sharpness = mask.conditional sharpness, max_sharpness
progress = "#{ "%3d" % i }/#{ "%3d" % stack_file.size }"
field_window.title = "Height field (#{progress})"
view_window.title = "Deep view (#{progress})"
field_output.write field * ( 255.0 / stack_file.size )
view_output.write view
display.process_events
end
field.save_ubyte field_file
view.save_ubytergb view_file
field_window.title = 'Height field'
view_window.title = 'Deep view'
display.event_loop
Line Fit
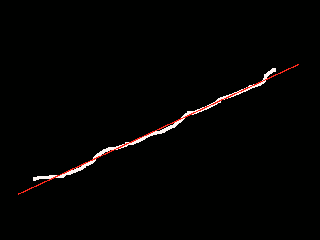
This program fits a line assuming that the input image is showing a single white line without outliers. The problem of ambiguity with the orientation of the line is overcome by estimating “2*a” instead of the angle “a”.
require 'hornetseye_rmagick'
require 'hornetseye_xorg'
include Hornetseye
class MultiArray
class << self
def cramp( w, h )
lazy( w, h ) { |i,j| i + Complex::I * j }
end
end
end
img = MultiArray.load_ubyte 'http://www.wedesoft.de/hornetseye-api/images/line.png'
x = MultiArray.cramp( *img.shape ).mask img >= 128
c = x.sum / x.size.to_f
a = Math.sqrt( ( ( x - c ) ** 2 ).sum / x.size )
gc = Magick::Draw.new
gc.stroke 'red'
gc.stroke_width 1
gc.line( ( c - 2 * a ).real, ( c - 2 * a ).imag,
( c + 2 * a ).real, ( c + 2 * a ).imag )
result = img.to_ubytergb.to_magick
gc.draw result
result.to_ubytergb.show
Hough Transform

The following example detects white lines in a black-and-white image using a Hough transform.
require 'multiarray'
require 'hornetseye_rmagick'
require 'hornetseye_xorg'
include Hornetseye
class Node
def nms( threshold = 0 )
finalise { dilate.major( threshold ) <= self }
end
end
A_RANGE = 0 .. 179
THRESHOLD = 128
img = MultiArray.load_ubyte 'http://www.wedesoft.de/hornetseye-api/images/lines.png'
diag = Math.sqrt( img.width ** 2 + img.height ** 2 )
d_range = -( diag + 1 ).div( 2 ) ... ( diag + 1 ).div( 2 )
binary = img >= THRESHOLD
x = lazy( *img.shape ) { |i,j| i - img.width / 2 }.mask binary
y = lazy( *img.shape ) { |i,j| j - img.height / 2 }.mask binary
idx = lazy( A_RANGE.end + 1 ) { |i| i }
angle = lazy { Math::PI * idx / A_RANGE.end }
dist = lazy( d_range.end + 1 - d_range.begin ) { |i| i + d_range.begin }
cos, sin = lazy { |i| Math.cos( angle[ i ] ) }, lazy { |i| Math.sin( angle[ i ] ) }
a = lazy( angle.size, x.size ) { |i,j| i }
d = lazy { |i,j| ( x[j] * cos[i] + y[j] * sin[i] - d_range.begin ).to_int }
histogram = [ a, d ].histogram A_RANGE.end + 1, d_range.end + 1 - d_range.begin
peaks = histogram.nms 40
peaks.conditional( RGB( 255, 0, 0 ), histogram.normalise ).show
a = lazy( d_range.end + 1 - d_range.begin ) { |j| angle }.mask peaks
d = lazy( A_RANGE.end + 1 ) { |i| dist }.roll.mask peaks
x = lazy { |i,j| ( Math.cos( a[j] ) * d[j] - Math.sin( a[j] ) * dist[i] + img.width / 2 ).to_int }
y = lazy { |i,j| ( Math.sin( a[j] ) * d[j] + Math.cos( a[j] ) * dist[i] + img.height / 2 ).to_int }
m = lazy { ( x >= 0 ).and( x < img.shape[0] ).and( y >= 0 ).and( y < img.shape[1] ) }
( [ x.mask( m ), y.mask( m ) ].histogram( *img.shape ) > 0 ).
conditional( RGB( 255, 0, 0 ), img ).show
PCA Recognition

The example program performs two-dimensional object recognition with three degrees of freedom. This is a customised algorithm which only works on images showing a single object which can be detected using colour-segmentation. In a controlled environment however this algorithm can be very useful as it is easy to implement. This algorithm has become popular recently in the context of touchless interfaces.
require 'matrix'
require 'hornetseye_rmagick'
require 'hornetseye_v4l2'
require 'hornetseye_qt4'
include Hornetseye
class Node
def rgbabs
r.abs + g.abs + b.abs
end
end
class PCAWindow < Qt::Widget
SIZE2 = 20
def initialize
super
self.windowTitle = "PCA Recognition"
@xvideo = Hornetseye::XvWidget.new self
@slider = Qt::Slider.new Qt::Horizontal
@checkbox = Qt::CheckBox.new '&Freeze Reference', self
@slider.minimum = 0
@slider.value = 32
@slider.maximum = 128
layout = Qt::VBoxLayout.new self
layout.addWidget @xvideo
hlayout = Qt::HBoxLayout.new
hlayout.addWidget @slider
hlayout.addWidget @checkbox
layout.addLayout hlayout
@input = V4L2Input.new
@w, @h = @input.width, @input.height
resize @w, @h
@reference = RGB 128, 128, 128
@x, @y = lazy( @w, @h ) { |i,j| i }, lazy( @w, @h ) { |i,j| j }
@xx, @yy, @xy = @x ** 2, @y ** 2, @x * @y
@old_eigenvector = Vector[ 1, 0 ]
startTimer 0
end
def timerEvent( e )
img = @input.read_ubytergb
if not @checkbox.checked?
box = [ ( @w / 2 - SIZE2 )...( @w / 2 + SIZE2 ),
( @h / 2 - SIZE2 )...( @h / 2 + SIZE2 ) ]
area = img[ *box ]
@reference = area.sum / area.size
else
end
mask = ( img.to_sintrgb - @reference ).rgbabs < @slider.value
img = mask.conditional @reference / 2 + RGB( 128, 128, 128 ), img
if not @checkbox.checked?
img[ *box ] = 255 - area
else
n = mask.to_ubyte.sum
if n > 0
sum = Vector[ @x.mask( mask ).sum, @y.mask( mask ).sum ]
center = sum * ( 1.0 / n )
xx = @xx.mask( mask ).sum
yy = @yy.mask( mask ).sum
xy = @xy.mask( mask ).sum
squares = Matrix[ [ xx, xy ], [ xy, yy ] ]
covariance = ( n * squares - sum.covector.transpose * sum.covector ) /
( n ** 2 ).to_f
discriminant = ( covariance.trace ** 2 - 4 * covariance.determinant )
discriminant = 0.0 if discriminant < 0.0
# Take smallest eigenvalue. Eigenvalues are
# "0.5 * ( covariance.trace +- Math.sqrt( discriminant ) )"
lambda1 = 0.5 * ( covariance.trace - Math.sqrt( discriminant ) )
eigenspace = covariance - lambda1 * Matrix.unit( 2 )
# Compute eigenvector by projecting basis-vectors.
vector1 = eigenspace * Vector[ 1, 0 ] - Vector[ 1, 0 ]
vector2 = eigenspace * Vector[ 0, 1 ] - Vector[ 0, 1 ]
if vector1.r >= vector2.r
eigenvector = vector1 * ( 1.0 / vector1.r )
else
eigenvector = vector2 * ( 1.0 / vector2.r )
end
# Resolve ambiguity by comparing with previous eigenvector.
if @old_eigenvector.inner_product( eigenvector ) < 0
eigenvector = eigenvector.collect { |x| -x }
end
@old_eigenvector = eigenvector
gc = Magick::Draw.new
pointer = center + eigenvector * 30
gc.fill_opacity( 0 ).stroke( 'blue' ).stroke_width( 3 )
gc.circle( center[0], center[1], pointer[0], pointer[1] )
gc.line( center[0], center[1], pointer[0], pointer[1] )
img = img.to_ubytergb.to_magick
gc.draw img
img = img.to_ubytergb
end
end
@xvideo.write img
end
def keyPressEvent( event )
case event.key
when Qt::Key_Escape
close
else
super event
end
end
end
app = Qt::Application.new ARGV
PCAWindow.new.show
app.exec
Power Spectrum
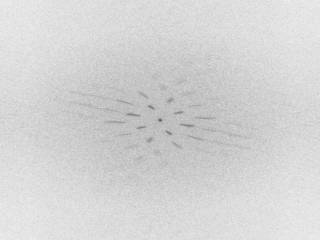
The following example demonstrates using windowing, zero padding, and Fourier transform in order to compute the power spectrum of a signal. The example image shows the power spectrum of a piece of fabric.
require 'hornetseye_fftw3'
require 'hornetseye_rmagick'
require 'hornetseye_xorg'
include Hornetseye
class Node
def window
finalise do |i,j|
x = ((i + 0.5 - 0.5 * width ) / (0.5 * width )).abs
y = ((j + 0.5 - 0.5 * height) / (0.5 * height)).abs
w = (1 - Math.sqrt(x ** 2 + y ** 2)).major 0.0
self[i,j] * w
end
end
def zeropad
retval = MultiArray.new(typecode, 2 * width, 2 * height).fill!
retval[0 ... width, 0 ... height] = self
retval
end
def spectrum
fft = window.zeropad.fft
(fft.conj * fft).real
end
end
img = MultiArray.load_ubyte 'http://www.wedesoft.de/hornetseye-api/images/texture.jpg'
(img.spectrum ** 0.1).shift(*img.shape).normalise(255 .. 0).show *img.shape
Phase Correlation
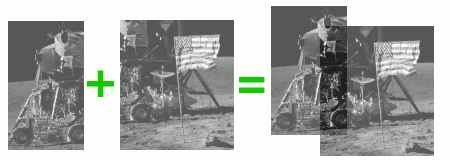
This is an implementation of the phase correlation for aligning images. This implementation also works on images which are of different size. I.e. stitching of overlapping images is possible as well as searching a small template in a large image. Note that you may have to add a windowing function to the implementation to avoid boundary effects.
require 'hornetseye_fftw3'
require 'hornetseye_rmagick'
require 'hornetseye_xorg'
include Hornetseye
class Node
def zeropad( *s )
retval = MultiArray.new( typecode, *s ).fill!
retval[ 0 ... shape[0], 0 ... shape[1] ] = self
retval
end
def phase_corr_cyclical( other )
nominator = rfft * other.rfft.conj
denominator = nominator.abs
mask = denominator.abs > 1.0e-5
( nominator.mask( mask ) / denominator.mask( mask ) ).unmask( mask ).irfft
end
def phase_corr( other )
ext_shape = [ shape[0] + other.shape[0], shape[1] + other.shape[1] ]
zeropad( *ext_shape ).phase_corr_cyclical other.zeropad( *ext_shape )
end
end
syntax = <<END_OF_STRING
Align images using phase correlation
Syntax : pc.rb <image1> <image2>
Example: pc.rb image1.jpg image2.jpg
END_OF_STRING
if ARGV.size != 2
puts syntax
raise "Wrong number of command-line arguments"
end
image = MultiArray.load_ubyte ARGV[0]
template = MultiArray.load_ubyte ARGV[1]
shift = image.phase_corr template
shiftx, shifty = argmax { |i,j| shift[i,j] }
shiftx = shiftx - image.shape[0] - template.shape[0] if shiftx > image.shape[0]
shifty = shifty - image.shape[1] - template.shape[1] if shifty > image.shape[1]
minx = [ 0, shiftx ].min
miny = [ 0, shifty ].min
maxx = [ image.shape[0], template.shape[0] + shiftx ].max - 1
maxy = [ image.shape[1], template.shape[1] + shifty ].max - 1
offsetx = -minx
offsety = -miny
resultwidth = maxx + 1 - minx
resultheight = maxy + 1 - miny
result1 = MultiArray.ubyte( resultwidth, resultheight ).fill!
result1[ offsetx ... offsetx + image.shape[0],
offsety ... offsety + image.shape[1] ] = image / 2
result2 = MultiArray.ubyte( resultwidth, resultheight ).fill!
result2[ shiftx + offsetx ... shiftx + offsetx + template.shape[0],
shifty + offsety ... shifty + offsety + template.shape[1] ] = template / 2
( result1 + result2 ).show
Normalised Cross-Correlation

This is an implementation of the normalised cross-correlation for locating a template in an image. The template must be smaller than the image. Note that the implementation could be optimised using integral images.
require 'hornetseye_fftw3'
require 'hornetseye_rmagick'
require 'hornetseye_xorg'
include Hornetseye
class Node
def avg
sum / size
end
def sqr
self * self
end
def corr(other)
(rfft * other.rfft.conj).irfft
end
def zcorr(other)
zother = MultiArray.dfloat(*shape).fill!
zother[0 ... other.shape[0], 0 ... other.shape[1]] = other
corr zother
end
def ma(*box)
iself = MultiArray.dfloat(*shape).fill!
iself[1 ... shape[0], 1 ... shape[1]] = self[0 ... shape[0] - 1, 0 ... shape[1] - 1]
int = iself.integral
int[0 ... shape[0] - box[0], 0 ... shape[1] - box[1]] +
int[box[0] ... shape[0], box[1] ... shape[1]] -
int[0 ... shape[0] - box[0], box[1] ... shape[1]] -
int[box[0] ... shape[0], 0 ... shape[1] - box[1]]
end
def ncc(other, noise)
box = other.shape
zcorr(other - other.avg)[0 ... shape[0] - box[0], 0 ... shape[1] - box[1]] /
Math.sqrt((sqr.ma(*other.shape) -
ma(*other.shape).sqr / other.size) *
(other - other.avg).sqr.sum + noise)
end
end
syntax = <<END_OF_STRING
Locate template using normalised cross-correlation
Syntax : ncc.rb <image> <template>
Example: ncc.rb image.jpg template.jpg
END_OF_STRING
if ARGV.size != 2
puts syntax
raise "Wrong number of command-line arguments"
end
image = MultiArray.load_ubyte ARGV[0]
template = MultiArray.load_ubyte ARGV[1]
ncc = image.to_dfloat.ncc template.to_dfloat, 0.1
shiftx, shifty = argmax { |i,j| ncc[i,j] }
result1 = image / 2
result2 = MultiArray.ubyte(*image.shape).fill!
result2[shiftx ... shiftx + template.shape[0],
shifty ... shifty + template.shape[1]] = template / 2
(result1 + result2).show
Camshift Tracking

This is an implementation of the Camshift algorithm for real-time tracking. The algorithm tracks the object by maximising the similarity of a hue reference histogram and a hue scene histogram.
require 'hornetseye_v4l2'
require 'hornetseye_xorg'
include Hornetseye
WIDTH = 320
BOX_SIZE = 64
SHIFT = 3
N = 0x100 >> SHIFT
RANGE = 0x30 .. 0xD0
MAX_ITER = 5
RATIO = 1.2
HUE = finalise N, N, N do |x,y,z|
r, g, b = ( x + 0.5 ) / N, ( y + 0.5 ) / N, ( z + 0.5 ) / N
min = r.minor( g ).minor b
max = r.major( g ).major b
max.eq( min ).
conditional( 0,
max.eq( r ).and( g >= b ).
conditional( 60 * ( g - b ) / ( max - min ),
max.eq( r ).and( g < b ).
conditional( 60 * ( g - b ) / ( max - min ) + 360,
max.eq( g ).
conditional( 60 * ( b - r ) / ( max - min ) + 120,
60 * ( r - g ) / ( max - min ) + 240 ) ) ) )
end
SAT = finalise N, N, N do |x,y,z|
r, g, b = ( x + 0.5 ) / N, ( y + 0.5 ) / N, ( z + 0.5 ) / N
min = r.minor( g ).minor b
max = r.major( g ).major b
max.eq( 0 ).conditional 0, 255 * ( max - min ) / max
end
MIN = finalise N, N, N do |x,y,z|
r, g, b = ( x + 0.5 ) / N, ( y + 0.5 ) / N, ( z + 0.5 ) / N
r.minor( g ).minor b
end
MAX = finalise N, N, N do |x,y,z|
r, g, b = ( x + 0.5 ) / N, ( y + 0.5 ) / N, ( z + 0.5 ) / N
r.major( g ).major b
end
input = V4L2Input.new do |modes|
modes.select { |mode| mode[0].rgb? }.sort_by { |mode| (mode[1] - WIDTH).abs }.first
end
box = [ ( input.width - BOX_SIZE ) / 2 ... ( input.width + BOX_SIZE ) / 2,
( input.height - BOX_SIZE ) / 2 ... ( input.height + BOX_SIZE ) / 2 ]
reference = nil
X11Display.show :title => 'Capture Reference Histogram' do
img = input.read_ubytergb.flip 0
reference = img[ *box ].dup
img[ *box ] = 0x80 + ( reference >> 1 )
img
end
histogram = ( reference >> SHIFT ).lut( HUE.to_usint ).histogram 360
flesh_map = ( MIN >= RANGE.begin / 256.0 ).and( MAX <= RANGE.end / 256.0 ).
conditional( HUE.to_usint.lut( histogram ), 0 )
cx, cy = input.width / 2, input.height / 2
w, h = BOX_SIZE, ( BOX_SIZE * RATIO ).to_i
X11Display.show :title => 'Camshift' do
image = input.read_ubytergb.flip 0
n = 0
sum = 0
begin
region = image[ cx - w / 2 ... cx - w / 2 + w, cy - h / 2 ... cy - h / 2 + h ]
weight = ( region >> SHIFT ).lut flesh_map
old_sum = sum
sum = weight.sum
if sum > 0
dx = sum { |i,j| weight[ i, j ] * i } / sum
dy = sum { |i,j| weight[ i, j ] * j } / sum
cx = cx + dx - w / 2
cy = cy + dy - h / 2
s = 2 * Math.sqrt( sum / flesh_map.max.to_f / RATIO )
w, h = s.to_i, ( s * RATIO ).to_i
w = [ [ w, 3 ].max, input.width ].min
h = [ [ h, 3 ].max, input.height ].min
cx = [ [ cx, w / 2 ].max, input.width - w + w / 2 ].min.to_i
cy = [ [ cy, h / 2 ].max, input.height - h + h / 2 ].min.to_i
end
n += 1
end while old_sum < sum and n < MAX_ITER
image[ cx - w / 2 ... cx - w / 2 + w, cy - h / 2 ... cy - h / 2 + h ] /= 2
image
end
Lucas-Kanade Tracker
![]()
This is an implementation of the (inverse compositional) Lucas-Kanade algorithm. The Lucas-Kanade algorithm iteratively tries to minimise the difference between the template and a warped image. The technique can be used for image alignment, tracking, optic flow analysis, and motion estimation. Possible improvements are to incorporate illumination changes and a proper threatment of the image boundaries.
The example offers five different models
- shift
- shift and scale
- shift and rotation
- affine transform
- 2-d homography
A video for testing can be created using PovRay and the files polygon.ini and polygon.pov.
require 'matrix'
require 'hornetseye_ffmpeg'
require 'hornetseye_rmagick'
require 'hornetseye_xorg'
#require 'matrix_fix'
include Hornetseye
syntax = <<END_OF_STRING
Align images using phase correlation
Syntax: lktracker.rb <video> <backgr.> <model> <width> <height> <p1> <p2> ...
Examples:
./lktracker.rb polygon.avi shift 94 65 80 35
./lktracker.rb polygon.avi shift-n-scale 94 65 80 35 1 1
./lktracker.rb polygon.avi isometry 94 65 80 35 0
./lktracker.rb polygon.avi rotate-n-scale 94 65 80 35 0 1
./lktracker.rb polygon.avi affine 94 65 80 35 1 0 0 1
./lktracker.rb polygon.avi homography 94 65 1 0 0 1 80 35 0 0
END_OF_STRING
if ARGV.size < 2
puts syntax
raise 'Wrong number of command-line arguments'
end
class Node
def warp_clipped_interpolate( x, y )
x0 = x.floor.to_int
y0 = y.floor.to_int
x1 = x0 + 1
y1 = y0 + 1
fx1 = x - x0
fy1 = y - y0
fx0 = x1 - x
fy0 = y1 - y
return warp( x0, y0 ) * fx0 * fy0 +
warp( x1, y0 ) * fx1 * fy0 +
warp( x0, y1 ) * fx0 * fy1 +
warp( x1, y1 ) * fx1 * fy1
end
end
input = AVInput.new ARGV[0]
w, h = ARGV[2].to_i, ARGV[3].to_i
case ARGV[1]
when 'shift'
raise 'Shifting model requires 2 parameters' if ARGV.size != 6
p = Vector[ *ARGV[4...6].collect { |a| a.to_f } ]
def model( p, x, y )
Vector[ x + p[0], y + p[1] ]
end
def derivative( x, y ) # derivative at p = [ 0, 0 ]
Matrix[ [ 1, 0 ], [ 0, 1 ] ]
end
def compose( p, d )
p + d
end
when 'shift-n-scale'
raise 'Shift-and-scale model requires 4 parameters' if ARGV.size != 8
p = Vector[ *ARGV[4...8].collect { |a| a.to_f } ]
def model( p, x, y )
Vector[ x * p[2] + p[0], y * p[3] + p[1] ]
end
def derivative( x, y ) # derivative at p = [ 0, 0, 1, 1 ]
Matrix[ [ 1, 0 ], [ 0, 1 ], [ x, 0 ], [ 0, y ] ]
end
def compose( p, d )
p + Vector[ p[2] * d[0], p[3] * d[1], p[2] * d[2], p[3] * d[3] ]
end
when 'isometry'
raise 'Isometric model requires 3 parameters' if ARGV.size != 7
p = Vector[ *ARGV[4...7].collect { |a| a.to_f } ]
def model( p, x, y )
cw, sw = Math::cos( p[2] ), Math::sin( p[2] )
Vector[ x * cw - y * sw + p[0], x * sw + y * cw + p[1] ]
end
def derivative( x, y ) # derivative at p = [ 0, 0, 0 ]
Matrix[ [ 1, 0 ], [ 0, 1 ], [ -y, x ] ]
end
def compose( p, d )
cw, sw = Math::cos( p[2] ), Math::sin( p[2] )
p + Matrix[ [ cw, -sw, 0 ],
[ sw, cw, 0 ],
[ 0, 0, 1 ] ] * d
end
when 'rotate-n-scale'
raise 'Isometric model requires 3 parameters' if ARGV.size != 8
p = Vector[ *ARGV[4...8].collect { |a| a.to_f } ]
def model( p, x, y )
cw, sw, s = Math::cos( p[2] ), Math::sin( p[2] ), p[3]
Vector[ x * cw * s - y * sw * s + p[0], x * sw * s + y * cw * s + p[1] ]
end
def derivative( x, y ) # derivative at p = [ 0, 0, 0 ]
Matrix[ [ 1, 0 ], [ 0, 1 ], [ -y, x ], [ x, y ] ]
end
def compose( p, d )
cw, sw, s = Math::cos( p[2] ), Math::sin( p[2] ), p[3]
p + Matrix[ [ cw, -sw, 0, 0 ],
[ sw, cw, 0, 0 ],
[ 0, 0, 1, 0 ],
[ 0, 0, 0, 1 ] ] * d
end
when 'affine'
raise 'Affine model requires 6 parameters' if ARGV.size != 10
p = Vector[ *ARGV[4...10].collect { |a| a.to_f } ]
def model( p, x, y )
Vector[ x * p[2] + y * p[4] + p[0], x * p[3] + y * p[5] + p[1] ]
end
def derivative( x, y ) # derivative at p = [ 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1 ]
Matrix[ [ 1, 0 ], [ 0, 1 ], [ x, 0 ], [ 0, x ], [ y, 0 ], [ 0, y ] ]
end
def compose( p, d )
p + Matrix[ [ p[2], p[4], 0, 0, 0, 0 ],
[ p[3], p[5], 0, 0, 0, 0 ],
[ 0, 0, p[2], p[4], 0, 0 ],
[ 0, 0, p[3], p[5], 0, 0 ],
[ 0, 0, 0, 0, p[2], p[4] ],
[ 0, 0, 0, 0, p[3], p[5] ] ] * d
end
when 'homography'
raise 'Homography requires 8 parameters' if ARGV.size != 12
p = Vector[ *ARGV[4...12].collect { |a| a.to_f } ]
def model( p, x, y )
h = Matrix[ [ p[0], p[2], p[4] ],
[ p[1], p[3], p[5] ],
[ p[6], p[7], 1 ] ]
rh = h * Vector[ x, y, 1 ]
Vector[ rh[0] / rh[2], rh[1] / rh[2] ]
end
def derivative( x, y )
Matrix[
[ x, 0 ], [ 0, x ], [ y, 0 ], [ 0, y ], [ 1, 0 ], [ 0, 1 ],
[ -x * x, -x * y ], [ -y * x, -y * y ] ]
end
def compose( p, d )
h = Matrix[ [ p[0], p[2], p[4] ],
[ p[1], p[3], p[5] ],
[ p[6], p[7], 1 ] ]
hd = Matrix[ [ 1 + d[0], d[2], d[4] ],
[ d[1], 1 + d[3], d[5] ],
[ d[6], d[7], 1 ] ]
hr = h * hd
hr = hr / hr[2,2]
Vector[ hr[0,0], hr[1,0], hr[0,1], hr[1,1],
hr[0,2], hr[1,2], hr[2,0], hr[2,1] ]
end
else
raise "No such model (#{ARGV[1]})"
end
img = input.read_ubyte
sigma = 2.5
# compute gradient on a larger field and crop later to avoid fringe effects.
b = ( Array.gauss_gradient_filter( sigma ).size - 1 ) / 2
x = lazy( w + 2 * b, h + 2 * b ) { |i,j| i - b }
y = lazy( w + 2 * b, h + 2 * b ) { |i,j| j - b }
tpl = img.warp_clipped_interpolate *model( p, x, y )
gx = tpl.gauss_gradient( sigma, 0 )
gy = tpl.gauss_gradient( sigma, 1 )
tpl, gx, gy, x, y = *( [ tpl, gx, gy, x, y ].collect { |arr| arr[ b...(w+b), b...(h+b) ] } )
c = derivative( x, y ) * Vector[ gx, gy ]
hs = ( c * c.covector ).collect { |e| e.sum }
hsinv = hs.inverse
X11Display.show :title => 'Lucas-Kanade tracker' do
img = input.read_ubyte
for i in 0...5
diff = tpl - img.warp_clipped_interpolate( *model( p, x, y ) )
s = c.collect { |e| ( e * diff ).sum }
p = compose( p, hsinv * s )
end
gc = Magick::Draw.new
gc.fill_opacity 0
gc.stroke( 'red' ).stroke_width 1
gc.line *( model( p, 0, 0 ).to_a + model( p, w, 0 ).to_a )
gc.line *( model( p, 0, h ).to_a + model( p, w, h ).to_a )
gc.line *( model( p, 0, 0 ).to_a + model( p, 0, h ).to_a )
gc.line *( model( p, w, 0 ).to_a + model( p, w, h ).to_a )
gc.circle *( model( p, 0, 0 ).to_a + model( p, 3, 0 ).to_a )
result = img.to_ubytergb.to_magick
gc.draw result
result.to_ubytergb
end
EAN-13 Barcode Reader

The example below is a barcode reader for reading EAN-13 (and UPC) barcodes. Reading of the barcode is restricted to a single line of the camera image. However the application can read barcodes forwards as well as backwards. The detected numbers are displayed using RMagick.
require 'hornetseye_v4l2'
require 'hornetseye_xorg'
require 'hornetseye_rmagick'
include Hornetseye
class Integer
def checksum
x = self / 10
retval = 0
while x > 0
retval += ( x % 10 ) * 3
x /= 10
retval += x
x /= 10
end
retval = retval % 10
retval = 10 - retval unless retval == 0
retval
end
def check?
checksum == self % 10
end
end
input = V4L2Input.new { |modes| modes.sort_by { |mode| ( mode[1] - 640 ).abs }.first }
SIGMA = 20.0
NOISE = 10.0
ERR_THRESH = 0.25
WIDTH, HEIGHT = input.width, input.height
result = MultiArray.ubytergb WIDTH, HEIGHT + 100
result[ HEIGHT ... HEIGHT + 100 ] = 128
segment = Sequence[ *( [ 0 ] * 3 +
( 1 .. 6 ).collect { |i| [ i ] * 4 }.flatten +
[ 7 ] * 5 +
( 8 .. 13 ).collect { |i| [ i ] * 4 }.flatten +
[ 14 ] * 3 ) ]
digits = MultiArray[ [ [ 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1 ],
[ 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1 ],
[ 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1 ],
[ 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1 ],
[ 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1 ],
[ 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1 ],
[ 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1 ],
[ 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1 ],
[ 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1 ],
[ 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1 ] ],
[ [ 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1 ],
[ 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1 ],
[ 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1 ],
[ 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1 ],
[ 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1 ],
[ 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1 ],
[ 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1 ],
[ 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1 ],
[ 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1 ],
[ 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1 ] ],
[ [ 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0 ],
[ 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0 ],
[ 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0 ],
[ 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0 ],
[ 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0 ],
[ 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0 ],
[ 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0 ],
[ 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0 ],
[ 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0 ],
[ 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0 ] ] ].to_byte
patterns = MultiArray[ [ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2 ],
[ 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2 ],
[ 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2 ],
[ 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2 ],
[ 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2 ],
[ 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2 ],
[ 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2 ],
[ 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2 ],
[ 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2 ],
[ 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2 ] ].to_byte
X11Display.show do
img = input.read_ubyte
avg = img[ HEIGHT / 2 ]
mean = avg.gauss_blur SIGMA
var = Math.sqrt( ( ( avg - mean ) ** 2 ).gauss_blur( SIGMA ) )
binary = ( avg < mean ).and( var >= NOISE )
up = binary.to_ubyte.convolve( Sequence[ 1, -1 ] ).major 0
down = binary.to_ubyte.convolve( Sequence[ -1, 1 ] ).major 0
stripe = ( up + down ).integral
n = up.sum
views = Sequence.int( avg.size ).fill! 128
zebra = Sequence.ubyte( avg.size ).fill! 128
for o in 0 .. n - 30
msk = ( stripe >= 2 * o + 1 ).and stripe <= 2 * o + 59
range = lazy( WIDTH ) { |i| i }.mask( msk ).range
views += msk.to_ubyte
code = ( stripe[ range ] - 2 * o - 1 ).lut segment
sequence = binary[ range ]
s = sequence.mask( code.eq( 0 ) ).to_byte
m = sequence.mask( code.eq( 7 ) ).to_byte
e = sequence.mask( code.eq( 14 ) ).to_byte
c = Sequence[ 0, *( [ 1 ] * 6 + [ 0 ] + [ 1 ] * 6 + [0] ) ].to_bool
skew = code.histogram( 15 ).mask( c ).range
if skew.max < skew.min * 1.3
s_ = Sequence[ 1, 0, 1 ].warp lazy( s.size ) { |i| i * 3 / s.size }
m_ = Sequence[ 0, 1, 0, 1, 0 ].warp lazy( m.size ) { |i| i * 5 / m.size }
e_ = Sequence[ 1, 0, 1 ].warp lazy( e.size ) { |i| i * 3 / e.size }
if ( s - s_ ).abs.sum < s.size * ERR_THRESH and
( m - m_ ).abs.sum < m.size * ERR_THRESH and
( e - e_ ).abs.sum < m.size * ERR_THRESH
zebra = ( ( code % 2 ) * 255 ).unmask msk, :default => 128
number = Hash.new 0
max_err = Hash.new 0.0
exp = { :forward => 11, :backward => 0 }
( ( 1 .. 6 ).to_a + ( 8 .. 13 ).to_a ).each do |k|
cut = sequence.mask code.eq( k )
d = { :forward => cut, :backward => cut.flip( 0 ) }
span = lazy( cut.size ) { |i| i * 7 / cut.size }
d_ = digits.roll.warp( span ).unroll
[ :forward, :backward ].each do |dir|
err = ( 0 ... 3 ).collect do |lgr|
sum { |i| lazy { |j| ( d[ dir ].to_byte[ i ] - d_[ lgr ][ j ][ i ] ).abs } }
end
for i in 0 .. 9
lgr = patterns[ i ][ 11 - exp[ dir ] ]
match = argmin { |i| err[ lgr ][i] }.first
max_err[ [ dir, i ] ] = [ max_err[ [ dir, i ] ], err[ lgr ][ match ].to_f / cut.size ].max
number[ [ dir, i ] ] += match * 10 ** exp[ dir ]
end
end
exp[ :forward ] -= 1
exp[ :backward ] += 1
end
opt = max_err.min { |x,y| x[1] <=> y[1] }.first
number, max_err = number[ opt ] + opt[1] * 10 ** 12, max_err[ opt ]
if max_err < ERR_THRESH and number.check?
text = Magick::Image.new 100, 20
draw = Magick::Draw.new
draw.gravity Magick::CenterGravity
draw.text 0, 0, "%013d" % number
draw.draw text
result[ 0 ... WIDTH - text.columns, HEIGHT + 80 ... HEIGHT + 100 ] =
result[ text.columns ... WIDTH, HEIGHT + 80 ... HEIGHT + 100 ]
result[ WIDTH - text.columns ... WIDTH, HEIGHT + 80 ... HEIGHT + 100 ] =
text.to_ubytergb
break
end
end
end
end
result[ 0 ... WIDTH, 0 ... HEIGHT ] = img
result[ HEIGHT / 2 ] = ~img[ HEIGHT / 2 ]
result[ 0 ... WIDTH, HEIGHT ... HEIGHT + 20 ].roll[] = avg
result[ 0 ... WIDTH, HEIGHT + 20 ... HEIGHT + 40 ].roll[] = binary.not.to_ubyte * 255
result[ 0 ... WIDTH, HEIGHT + 40 ... HEIGHT + 60 ].roll[] = views.normalise
result[ 0 ... WIDTH, HEIGHT + 60 ... HEIGHT + 80 ].roll[] = zebra
result
end
See Also
External Links
- Gnuplot
- Ruby Gnuplot
- trollop
- Camshift publication
- Camshift video
- European Article Number
- Universal Product Code
- UPC database
- EAN-13 reader video
- PCA recognition video
- Camspace (play games with your webcam)
- Hough transform
- Lucas-Kanade 20 Years on: A Unifying Framework
- A machine vision extension for the Ruby programming language
- NASA high definition videos
- Fast Normalised Cross-Correlation